27.10.2016
2016-10-27
Sergey Semenov
76
The contents
The description of the disease
Reasons
Symptoms
Atypical forms of appendicitis
What to do if you suspect appendicitis?
Diagnosis
Treatment
Appendicitis is the most common surgical disease of the digestive system, and one of the most dangerous. The danger of the disease lies primarily in its transience and the inevitability of the emergence of serious, life-threatening complications. The probability to face acute appendicitis in the course of life is quite high. It is diagnosed in 5-10% of people.
Appendicitis can occur at any age and in people of either sex. However, statistics show that most often it becomes inflamed in people aged 5-40 years. Among patients aged 20-40 years are twice more women than men, while among patients under 20 years are male dominated. Women in General suffer more often than men. After 40 years the probability of occurrence of the disease is significantly reduced but does not become zero. Therefore, appendicitis can occur in older people. Also appendicitis is rarely diagnosed in children younger than 5 years.
The description of the disease
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the vermiform Appendix – the Appendix located in the lower part of the intestine. In normal condition the Appendix is a small tube with a diameter of 7-10 mm and a length of 50-150 mm. It branches off from the cecum, while gradually tapering, and has no through traffic.
The function of the Appendix has not been exactly clarified. Before the Appendix was considered a mere rudiment, derived by man from his distant ancestors of animals with herbivorous diet, and now functionally useless. Now there are serious grounds to believe that it plays an important role in endocrine and immune processes and in the formation of the intestinal microflora. It is proven that people with removed appendixes have problems with a sufficient quantity of beneficial microorganisms in the intestines. However, the Appendix is not a vital organ without which the organism cannot exist.
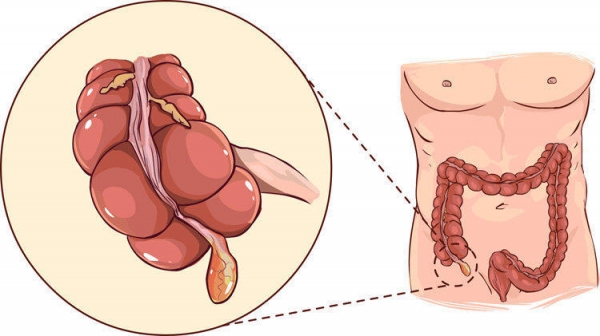
Photo: corbac40/Shutterstock.com
As a rule inflammation of the Appendix is acute. As a result of disease in the bone accumulates pus, which are not free to go outside because of the narrowness of the Appendix. The Appendix grows in size and becomes painful. This ultimately leads to rupture of the wall of the Appendix and release the pus out. This, in turn, entails acute peritonitis (inflammation of peritoneum), sepsis or abscesses in the abdominal cavity, which with a high degree of probability can lead to death. The most severe complication is pylephlebitis – leading to severe liver inflammation of the portal vein, in which the mortality rate is particularly high.
The disease progresses very quickly and usually lasts 2-4 days rarely more than a week. Cases of spontaneous cure of acute appendicitis are infrequent. Sometimes around the affected Appendix may form a protective infiltration of the surrounding tissues, but this education can also lead to an abscess. Therefore, the disease requires medical intervention and surgical treatment. With timely treatment of the disease the prognosis is favorable.
Occasionally and chronic appendicitis, characterized by the appear, then again retreating symptoms common to acute appendicitis. The incidence of this condition is about 100 times less common than acute. As a rule, it does not require surgical treatment.
Acute appendicitis divided into simple (catarrhal) destructive and fraught with complications. Without proper treatment of simple appendicitis almost always turns into destructive.
The main stages of development of appendicitis:
- Catarrhal
- Abscess
- Gangrenous
- Perforated
Reasons
Causes of appendicitis in adults is still uncertain. However, scientists agree that there is no one single cause of appendicitis that is common to all patients. Every patient the cause may be your own. In most cases appendicitis is caused by blockage of the entrance of the Appendix into the rectum. Causes of blockage can be different – for example, getting into the process of fecal stones or foreign bodies. It can be caused by squeezing the upper part of the Appendix due to adhesive processes resulting from cholecystitis or enteritis.
Also a big role in the occurrence of appendicitis are playing bacteria – enterococci, streptococci, staphylococci and Escherichia coli. Most often a combination of both. Stagnation of the contents of the Appendix leads to a weakening of its internal immunity and the introduction of pathogenic bacteria into the mucosa. There is also the theory that the main cause of appendicitis spasm of the vessels supplying the Appendix the blood. Another possible cause is injury to the abdomen resulting in damage or displacement of the Appendix.
The factors contributing to the disease include a tendency to constipation, poor peristalsis, lack of fiber in the diet, overeating, many infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, the presence of parasites. At the onset of the disease can be affected by hereditary factors as well as decreased immunity due to bad habits, stress, lack of vitamins and minerals.
Also observed an increased frequency of appendicitis in pregnant women because of the displacement of the Appendix, caused by an increase in size of the uterus. In the case of some diseases of the uterus may transfer with it of inflammation in the Appendix.
Symptoms

Photo: narikan/Shutterstock.com
For early diagnosis of appendicitis symptoms is crucial. Their knowledge allows to cut off other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract not related to appendicitis.
The main signs of appendicitis in adults include:
- Acute abdominal pain, including when pressed
- Temperature rise
- Nauseam
- Vomiting
The first symptoms and signs of acute appendicitis is not always possible to clearly identify the disease. Initially, the disease may masquerade as another, not so dangerous and the person may make an attack of appendicitis for renal colic or gastritis.
The main symptom of appendicitis constant pain in the abdomen. Usually, a sharp pain occurs suddenly, often at night or in the morning. In the catarrhal stage the pain is at first diffused throughout the abdomen or appears in its upper part (in the epigastric region). But then, the pain is in the lower right part of the abdomen, below the navel and just above the hip (iliac).
The process of moving the focus of pain is called symptom Kocher is one of the main defining characteristics of the disease. In most cases it testifies to appendicitis, and not any other disease of the gastrointestinal tract. This process occurs within several hours after onset of illness. The nature of pain over time are also changing, they are amplified and become throbbing and aching. The pain is worse when you laugh and cough, deep breath, a little quieter when turning to the right side or in the position when the legs bent to the stomach. The pain may also radiate into the right leg and be felt when walking. With pressure on the iliac area pain usually is almost not felt, however, releasing the abdomen, then severe pain occurs. Marked tension of the abdominal wall.
With the development of the disease the pain may at some time to subside. But it is not a cure, but just about the necrosis of the tissue wall of the Appendix, including its nerve endings. However, pressure on the iliac area is still extremely painful. After this stage usually occurs perforation of the wall, the pus spreads to the abdomen and back pain, enhanced many times over.
It should be borne in mind that sometimes the Appendix can be located on the left, so in this case, it will hurt the left part of the abdomen. In some cases, pain can be felt in the right hypochondrium, in region of pubis, pelvis, lumbar.
The symptoms of appendicitis in adults include disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. First of all, this nauseam. Sometimes you may experience diarrhea and vomiting, not bringing relief. However, diarrhea appendicitis is characterized first of all for children, in adults it is less common. Also marked constipation, a feeling of dryness in the mouth. Under unusual position of the Appendix may appear urinary retention (dysuria). Often marked tachycardia of 90-100 beats per minute.
In the initial phase of the disease the temperature rises slightly to +37-38 ºC. Subsequently, the temperature may even drop to normal, but in the final stage preceding the breakout of pus out, she again rises to high performance – +39-40 ºC. Pain significantly worse.
In the case of appendicitis in the elderly the symptoms can be erased and invisible until the transition of the disease in the destructive stage. Pain can wear a stupid character, nauseam to be small, and this feature, as fever may not be present. However, this does not mean that appendicitis occurs in older people easier. On the contrary, in old age much more frequently observed complications of appendicitis.
Difficult diagnosis of appendicitis and small children (under 5 years). This is due to the fact that signs of appendicitis in adults is usually expressed more clearly than in children. Sometimes appendicitis in a child disguised as a simple upset stomach. Pain is often not localized in the iliac region, and sometimes the child is unable to explain where he had a stomach ache. In this case, you should focus on such features as raising the temperature to +38 ° C, coated tongue, diarrhea. However, all these symptoms can appear in other diseases, so the child must be seen by a specialist.
Photo: plenoy m/Shutterstock.com
Atypical forms of appendicitis
Also there are several forms of atypical appendicitis in which the symptoms may differ from the standard.
- Empiema. Form of appendicitis with slow development in which the symptom Kocher is missing, and the pain appears in the right iliac region.
- Retrocecal appendicitis. Is characterized by weak signs of inflammation of the peritoneum, liquid stools. Pain is often felt in the lumbar region and irradiiruet in the thigh area.
- Left-sided appendicitis. Has a classic clinical picture, however, the pain is felt in the left iliac region.
- Pelvic appendicitis. More typical for women. There is little fever, dysuria, pain irradiiruet in the navel area.
What to do if you suspect appendicitis?
Upon the slightest suspicion of appendicitis should seek medical advice. Grounds for appeal to the doctor are any persistent pain in the abdomen, not passing for 6 hours. To medical examination should not take laxatives, antibiotics or other gastrointestinal drugs, particularly analgesics, since these drugs can lubricate the clinical picture and complicate the diagnosis. It is also forbidden to install hand warmers on the right side of the abdomen, as the external heat source is able to accelerate the development of the disease. Shown to bed. Should refrain from eating. With the arrival of the doctor should tell him about all the symptoms, how a stomach ache, and allow him to conduct the inspection.
Diagnosis
For diagnostic uses primarily visual inspection and palpation. The main symptoms are intense abdomen, tenderness in the right lower part. However, these methods are not always reliable. Are also used these diagnostics, such as ultrasound, MRI and computed tomography, blood tests and urine tests. When viewing the blood focuses on an increased level of leucocytes in blood (leucocytosis). May also perform diagnostic laparoscopic examination through a hole in the wall of the abdomen.
Note that detection of the disease can be difficult because symptoms of acute appendicitis is largely similar to other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. These include acute gastroenteritis, pancreatitis, ulcers (especially in case of perforation), intestinal or renal colic, inflammation of the uterus, sprain or rupture of abdominal muscles. Therefore, it is important to differentiate appendicitis from other diseases, most of which do not require urgent surgical intervention.
Treatment
Appendicitis is usually treated surgically. It consists in the removal of the Appendix (appendectomy surgery). In some cases it should be preceded by therapy with antibiotics. Sometimes it is possible and conservative treatment, without removal of the Appendix – in this case antibiotics are prescribed. Usually it is used if there are any contraindications to surgery.
The operation to remove the Appendix is carried out either in a traditional way, by means of an open incision or laparoscopically. The first 12 hours after surgery, you should stay in bed and avoid eating. The recovery period is also a possible therapy consequences of the disease with antibiotics. The recovery period depends on what stage of the disease the surgery was performed and usually lasts 1-2 weeks.
You can help:
All doctors
Artemova Svetlana Nikolaevna
4.8
Kiev
Sirazutdinova Zamira Hazratkulov
4.4
Ulitsa Akademika Yangelya
Karasev Diana G.
4.4
Kiev
Tags:

 BUY A WEBSITE
BUY A WEBSITE  BUY A WEBSITE
BUY A WEBSITE  BUY A WEBSITE
BUY A WEBSITE