16.06.2017
2017-06-16
Sergey Semenov
19
The contents
Preparation for assay biochemistry: how not to skew the results
Average values: normal adult
The values of total protein and fractions
Protein fractions
Nitrogen metabolism
The causes of fluctuations in the level of nitrogenous compounds
Carbohydrates in the blood
The causes of changes in the level of glucose
The pigments in the TANK
Bilirubin as an indicator of jaundice
- -left:40px;” class=”sub sub_1″>
In any cases assigned to the analysis on the fraction of bilirubin?
Analysis of lipid
Estimation of the amount of cholesterol
Causes of disorders of lipid metabolism
Analysis of enzymes
An analysis of the “liver function tests”
Alpha-amylase and pancreatic amylase
Creatine kinase and its fractions
Lipase
Types of phosphatase and their diagnostic value
Electrolytes
Potassium in the blood
Blood chemistry is a comprehensive laboratory diagnostics aimed at assessing the state of internal organs and systems and identify the body ‘ s need for minerals and the level of its satisfaction.
Biochemical parameters of the blood carry out initial diagnostics of the functioning of the liver, kidneys, pancreas, and other organs receive information about the metabolic processes (lipid, protein, carbohydrate metabolisms).
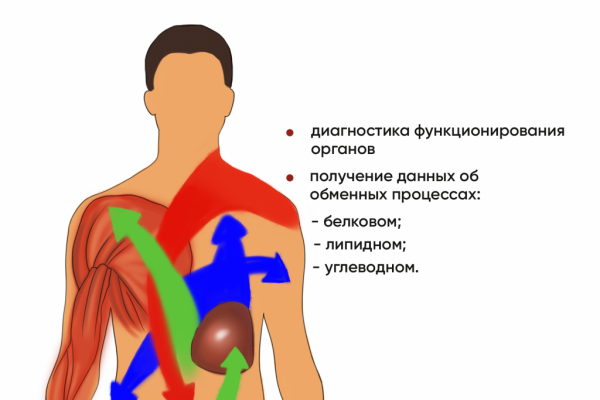
A undertake a detailed biochemical analysis of blood (TANK) recommended as a preventive measure for health monitoring and early diagnostics of diseases annually, and in developing somatic or infectious diseases, in the disease process at the stage of clinical recovery.
Interpretation of results of biochemical analysis carried out by the specialist on the basis of laboratory standards and their compliance with identified indicators. Independent transcript analyses often gives only a superficial understanding of the condition and can cause wrong self-diagnosis and subsequent self-medication, as in the interpretation of the results must consider not only demographic indicators but also the impact of the existing and illness, taking certain medicines that may affect blood composition, as well as to examine the picture of analysis in the complex: many indicators point to the existence of various processes, both physiological and pathological, and to correctly interpret the cause of changes in blood composition can only be a specialist. Often for the diagnosis after blood tests by this method, doctors prescribe additional tests for specification and differentiation of the causes revealed the condition of the patient.
Preparation for assay biochemistry: how not to skew the results
For the analysis in biochemistry using venous blood, approximately 5 ml, distributed in several tubes. Since the study includes indicators that may change due to the receipt of food, water, physical activity or neuro-emotional excitation, and also due to taking some medications, there are rules of preparation for blood donation for research. These include:
- hunger within 10-12 hours prior to blood sampling;
- exclusion from the diet in the second half of the previous analysis of the day coffee, strong brewed tea;
- light diet for 2-3 days prior to tests: it is advisable not to consume fatty, fried or spicy food, alcohol, etc.;
- during the previous day to avoid high physical activity and thermal procedures (bath, sauna, long hot bath).
- to donate blood you need to receive daily medications, for additional medical procedures and manipulations (injections, insert intravenous drugs, studies of physical methods – x-ray, fluoroscopy, etc., a visit to the dentist);
- on the day of blood sampling is necessary to refrain from physical activity, Jogging or long distance walking to lab. Any physical activity affect the blood picture and complicates the interpretation of the results;
- stress, nervous tension, as emotional arousal also may distort the results;
- before measurement it is necessary to sit quietly for 10 minutes and verify that the rhythm of breathing and heartbeats are normal;
- for accurate performance analysis of glucose, one of which is determined when the biochemistry of the factors especially important in the diagnosis of diabetes, it is necessary to abstain not only from the morning beverages (including water) and chewing gum, but teeth cleaning, especially with toothpaste. Taste buds contribute to the revitalization of the work of the pancreas and production of insulin;
- the day before analysis is not recommended to take hormonal drugs, diuretic, antibacterial, trommershauser actions drugs that affect blood viscosity, etc.;
- if necessary, diagnose the amount of cholesterol in the blood in patients receiving statin therapy (in coordination with the specialist) should be discontinued 10-14 days;
- if you want a second study to Refine the results, blood sampling should be made with as similar conditions: the same laboratory, time of day, until the route from home to the point of drawing blood (on foot or by transport).

Interesting fact:
Any human activity caused by biochemical processes in the body and, therefore, causes changes in the blood composition. Rules, which are guided by specialists in the interpretation of analysis made on the basis of a study of the influence of the average factors of blood collection occurs on an empty stomach, at rest, without prior action and enhance the digestive system. Sharp changes in the composition of blood will be noticeable and for distorted run for a bus or a morning Cup of coffee performance, but slightly exceeding the normal limit or approaching it, the results indicating the development of the disease can vary from non-compliance with rules of preparation for the analysis of biochemistry and lead to inaccurate and unreliable interpretation.
Average values: normal adult
The range of normal quantity contained in the blood of various substances is based on the study of statistical indicators of the study healthy people and patients with various diseases and pathologies. When interpreting, remember that the standards of the rules are different depending on age, some of the components there are specific standards for men and women. Under physiological conditions (e.g. pregnancy) of normal ranges are also shifted: for example, the amount of cholesterol in the gestational period may exceed the notional rate of two times, and the hemoglobin at a certain time of gestation decreased due to the increase in blood volume, and this is considered normal and not an indication for therapy.
To account for the influence of various factors in interpreting the results, it is recommended to consult a specialist assess General medical history of the patient and the blood picture is complex, and not only the results of the compliance index the rules in the table. Doctors say common symptoms, complaints, peculiarities of professional activity, history of diseases and genetic tendencies.
When evaluating results it is necessary to focus on the rules used in the particular laboratory, as laboratory equipment can estimate the amount of certain substances in different units of measurement – micrograms, mg per liter, percentage, etc. it is Especially important to consider this information when interpreting indicators of hepatic enzymes (alaninaminotransferase, aspartataminotransferase), where the results are affected by temperature of incubation of the sample which is usually indicated in the results form.
Some normal values for adults given in the table.
Figure
The unit of calculation
Valid values
Notes
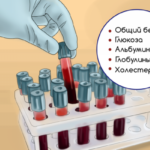
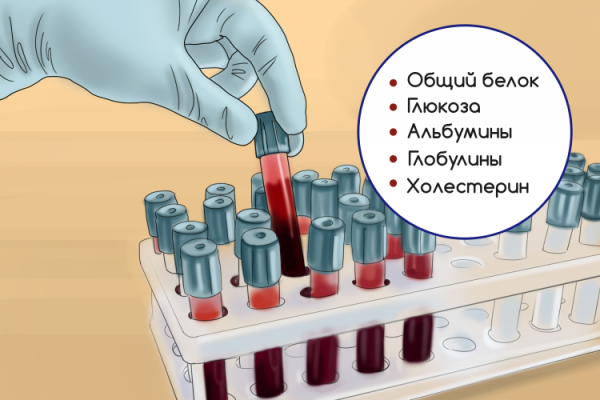
Protein total
Grams per liter
64-86
In children under 15 years of performance below the age norm
Albumin
Grams per liter or percentage of total protein
35-50 g/l
40-60 %
For children there are separate rules
Transferrin
Grams per liter
2-4
During pregnancy the rate increases in the elderly fall
Ferritin
Micrograms per liter
Men: 20-250
Female: 10-120
Adult men and women the norms are different
Total bilirubin
The unconjugated bilirubin is
Direct bilirubin
Micromol per liter
8,6-20,5
0-4,5
0-15,6
Selected indicators for children age
Alpha-fetoprotein
Unit per ml
0
Perhaps physiologically determined by the appearance of the factor in the 2-3 trimester of gestation
Globulin total
The percentage
40-60
Rheumatoid factor
Unit per ml
0-10
Regardless of age and gender characteristics
Expanded the biochemical analysis of blood can have many different indicators as recommended for regular preventive examinations, and specific study in cases of suspected specific diseases and disorders. In the expanded biochemistry, including the maximum number of studies in the analysis of the purpose of the screening is not necessary, as well as with individual complaints and symptoms. Additional common indicators of research performance components depend on the health of the patient: thus, with complaints of increased thirst will focus on the amount of glucose in the blood, high blood pressure and lipid spectrum, with symptoms of anemia, iron, transferrin, – ferritin, OSS (total iron-binding capacity the ability of serum), the signs of disturbance of the liver or the likelihood of hepatitis – hepatic enzymes (AST, ALT), indicators of bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase.
The values of total protein and fractions
In the results of clinical trials and TANK total chemical composition (cholesterol) blood always measure the quantity of total protein and its fractions – proteins. In General, the composition of blood contains more than 160 different proteins, combined in accordance with the composition and functions of three protein fractions: albumins, globulins (four types) and fibrinogenous.
All proteins are important for the effective functioning of the body. The main organ responsible for the production of proteins – the liver, and reduced relative to the norm of the amount of protein reflects the inability of the liver to synthesize proteins. This dysfunction may be associated with diseases and other conditions and factors, which include the impact of the following:
- a low protein diet (vegetarianism, fasting, and feeding habits restrictions of protein);
- parasitosis (mainly helminthic infestation);
- blood loss (profuse discharge during menstruation, internal and external bleeding after diseases and injuries);
- extensive burns of the cutaneous surface;
- excess secretion of proteins from the urine in kidney disease, proteinuria, gestational period, etc.;
- reduced protein synthesis by liver disease (hepatitis, cirrhosis);
- prolonged courses of therapy-corticosteroids;
- development of tumours (malignant tumours of the bladder, stomach);
- reduced absorption of nutrients in the intestine in enteritis, colitis, pancreatitis, celiac disease;
- diseases and abnormalities of structure, accompanied by accumulation of plasma (ascites, pleurisy, pericarditis).
Protein fractions
The concentration of albumin used in the diagnosis of pathologies in the parenchymal organs, the identification of rheumatic fever, signs of developing tumors, the effect of hormonal drugs on the body and consequences of fasts and diets.
While reduced rates of protein fractions of albumin may indicate nephrotic syndrome, hepatic or renal failure, tumors of the digestive system, the process of tissue decay, cardiospasm, simpore, paracentesis, depletion, etc.
Nitrogen metabolism
Urea, creatinine, uric acid, residual nitrogen, ammonia and some other blood components belong to the low molecular weight nitrogenous substances. In the base TANK exploring the values of urea and creatinine, adding more studies if there is suspicion for various disorders and diseases.
The causes of fluctuations in the level of nitrogenous compounds
Nitrogen compounds are produced by the decay of cells and tissues, the process inevitably accompanying the normal functioning of living organisms. Values exceeding the normal values often indicate a violation of the liver (where in the process of disintegration of synthesized nitrogenous substances), kidney (in case of accumulation of compounds in the body due to the reduced filtration and violations of the withdrawal of the urine) or increased disintegration of proteins for one reason or another.
The name of The connection
As indicated above the norm
Urea
Hepatic, renal failure, hypertension, compartment syndrome, exposure to toxic substances
Creatinine
Severe lesions and disease of the parenchymatous organs, adrenal dysfunction, tumor formation, diabetes mellitus
Uric acid
Gouty syndrome, leukemias, anemia with vitamin B12 deficiency, poisoning, dermatitis, acute infection, liver disease
The decrease in the number of nitrogenous compounds reported when polyuria, hepatic insufficiency, hypothyroidism, disorders of metabolism, prolonged fasting, and after procedures, hemodialysis and intravenous glucose solution.
Carbohydrates in the blood
The main marker of carbohydrate metabolism in the body is glucose (aka sugar). Most people know that it increased content indicates the presence of diabetes or prediabetes state. However, the cause of changes in the level of glucose can also be trauma, burns, passion, sweet, violations of the rules of preparation for analysis. Besides these obvious reasons for elevated glucose levels can occur in diseases of the pancreas and pathology of the liver.
In addition to glucose to identify impaired glucose metabolism resort to estimating the amount of glycated (or picolinafen) proteins: fructosamine (glycated albumin), glycated hemoglobin, glycated lipoprotein.
The causes of changes in the level of glucose
At the lowered glucose level diagnosed with hypoglycemia at elevated – hyperglycemia.
Possible causes of hypoglycemia
Possible causes of hyperglycemia
Inadequate nutrition, diet, fasting
1 diabetes, type 2
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, preventing the absorption of carbohydrates (colitis, enteritis, etc.)
Injuries, tumors of the brain (often the pituitary gland)
Hypothyroidism
Neoplastic growths, pathology of the adrenal cortex
Liver pathology
Thyrotoxicosis, thyroid disease
Prolonged uncontrolled intake insulinsoderjath drugs, drugs-of gipoglikemical
Epileptic syndrome
Encephalitis, meningoencephalitis, meningitis
Anxiety, unstable emotional state
Failure of function of the adrenal cortex
A long course of treatment with glucocorticosteroids
The pigments in the TANK
Some types of proteins have a specific colour, most often due to metals (iron, copper, chromium). In their decay in the blood bilirubin is released in indirect or free form. In subsequent processes it is converted to unavailable form. When assessing blood parameters there are three types hemoglobinemia pigment: total bilirubin, direct (linked, conjugated) bilirubin and the level of indirect (free, unbound, deconjugating). All three indicators are important and can indicate the presence of diseases and pathologies. Special attention to first of all pay for free bilirubin as it is toxic to the body.
Disease, encourage the growth of pigment in the blood, may range from genetic abnormalities to the effects of blood transfusions and transplantation of organs and tissues in the recipient. Diagnosis is based on the ratio of fractions of bilirubin. In most cases, exceeding the target of rules means the presence of liver diseases and/or pathologies of the biliary tract.
Bilirubin as an indicator of jaundice
After a chain of connections to change in the liver and the gallbladder, the bilirubin enters the intestine, where it is converted urobilinogen compound pigment, the derivation of body coloring the urine and feces.
In case of insufficiency of liver function or gall bladder pathologies and disorders of the biliary tract a significant portion of the conjugated bilirubin remains in the body, where, spreading through the tissues, gives them a yellow color. Due to this symptom the name “jaundice”, erroneously associated exclusively with hepatitis A. However, in clinical practice there are three types of processes that encourage the development of jaundice:
- toxic effects, poisoning, anemia, hemolytic etiology, pathological processes in the spleen, accompanied by its hyperfunction, accelerate the disintegration of the pigment protein and to increase the number of unbound bilirubin to quantities that do not have time to be processed in the liver and accumulate in blood and tissues;
- liver failure that occurs in hepatitis, cirrhosis, trauma, tumors of the liver in which the body is not able to handle the allotted amount of bilirubin;
- when violations of the outflow of bile from the gallbladder, accompanied by compression of the biliary tract, bilirubin re-enters the bloodstream and further into the tissue. This state is recorded in case of cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, acute cholangitis, tumours, preventing the bile flow, etc.
In any cases assigned to the analysis on the fraction of bilirubin?
Values of total bilirubin as standard TANK. A study on the level of fractions (unbound and conjugated bilirubin) is usually used in the presence of symptoms or diagnosed diseases: hepatitis of any etiology, cirrhosis, jaundice, etc.
Analysis of lipid
The concentrations of lipids (fats) in the blood are lipid spectrum. In diagnostic biochemical test to evaluate the level of total cholesterol, LDL and high-density (“bad” and “good” cholesterol), triglycerides, atherogenic coefficient and calculated based on the ratio of the components. In some cases to confirm the diagnosis, carry out the analysis on the number of phospholipids.
Estimation of the amount of cholesterol
Normal total cholesterol for a healthy adult is in the range of 3.0-5.2 mmol/l. From 40 to 60% of total cholesterol is “good” cholesterol. What is it?
In the body cholesterol is in two basic types, the high-molecular compound with proteins and low molecular weight. High-density lipoproteins is mainly produced in the liver and necessary for the body to participate in the formation of cell membranes, regulation of hormonal processes, emotional state, etc.
Lipoproteins low (and very low) density mainly come from food. These compounds have the property to accumulate in the blood vessels, forming cholesterol plaques (atherosclerosis). In consequence of the formation of such accumulations narrows the lumen of the vessel leading to reduced blood supply of organs and tissues. The destruction of lipoprotein concentrations of the fragments is also dangerous, as it can promote the formation of blood clots.
Causes of disorders of lipid metabolism
The increase in total cholesterol
Decrease total cholesterol
Eating disorders, obesity, diabetes mellitus, myocardial infarction, alcoholism, arterial hypertension, gestational period, ischemia, gallstone disease, etc.
Liver disease, hyperthyroidism, insufficiency of diet, disease of the gastrointestinal tract, preventing the absorption of lipids, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, rheumatoid arthritis
Analysis of enzymes
Most often a spectrum of enzymes in the biochemical test analysis is limited to “liver function tests”, Alt and AST, and amylase. In advanced analysis can include a much broader list of enzymes.
An analysis of the “liver function tests”
Indicators alaninaminotransferase (Alt) mainly characterize the efficiency of the functioning of the liver, but can also report violations of skeletal muscles and cardiac muscle.
Study of the level aspartataminotransferase (AST) is used in the diagnosis of diseases and pathologies of the liver and is used to detect cardiac pathologies (myocardial infarction, stenokardicheskie attack, rheumatic heart disease), some inflammatory processes of infectious etiology.
Alpha-amylase and pancreatic amylase
The enzyme responsible for the breakdown of complex carbohydrates. Diagnostic value have both increase and decrease of the concentration of amylase in relation to the norm.
In most cases, exceeded the normal amount of amylase in the blood accompanied by of the disease and the pathology of the pancreas. However, it can also be observed in hepatitis of viral etiology, endemic parotitis (“mumps”), renal failure, alcoholism, prolonged courses of therapy with tetracycline drugs, and corticosteroids.
Reduced rates noted under the following conditions and diseases:
- gestational toxicosis of the first trimester of pregnancy;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- myocardial infarction;
- necrotic processes in the pancreas.
Creatine kinase and its fractions
The enzyme creatine kinase allows to evaluate the efficiency of energy metabolism in muscle tissues (fraction of MM), cardiac muscle (MB) and brain tissue (BB). Diagnostic value has a high concentration of this enzyme, indicating an increased breakdown of tissue. Thus, the subtype of creatine kinase MB is used, for example, in diagnosing the presence of myocardial infarction, the assessment of the extensiveness of the lesions and predicting the situation.
Lipase
The lipase responsible for the breakdown of neutral fats. Pancreatic lipase is recognized as a more valuable indicator for the diagnosis of diseases of the pancreas than amylase and is used for diagnosis and extent of injury of the organ.
Types of phosphatase and their diagnostic value
There are two types of phosphatases: acid (analysis on the enzyme used in the differential diagnosis of bone diseases, liver diseases, pathologies of the biliary tract) and alkaline, a level which in most cases is manifested in diseases of the prostate.
Electrolytes
Despite the fact that the electrolytes in the blood are in pretty small quantities, the change in their concentrations can have damaging effects on the entire body and can lead to death. Main extracellular cation is sodium.
Sodium entering the body with food and fluids (sodium chloride – salt), responsible for the level of osmotic pressure in the tissues and acid-base balance. And high and low concentration of sodium in the blood can lead to minor changes in well-being and, depending on the concentration, to pathological conditions, and coma.
Potassium in the blood
An electrolyte, potassium is responsible for the conduction of electrical impulse in the cardiac muscle. And excess baggage, and reducing the concentration of potassium can lead to cardiac palpitations.
Tags:

 BUY A WEBSITE
BUY A WEBSITE  BUY A WEBSITE
BUY A WEBSITE  BUY A WEBSITE
BUY A WEBSITE